Run jupyter notebook online with AWS EC2
Source
https://medium.com/@alexjsanchez/python-3-notebooks-on-aws-ec2-in-15-mostly-easy-steps-2ec5e662c6c6
Requirement
- A AWS EC2’s instance
Setup EC2
Create EC2 instance
Choose AMI

Choose the instance’s type

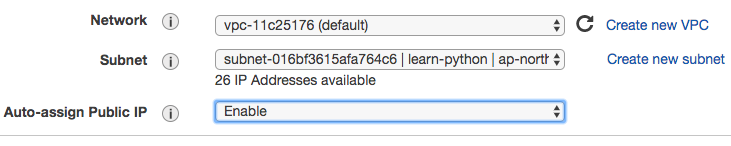
Setup network
You’ll need to place this instance in to public subnet and assign to it a public IP.
Create key or use existed key for ssh
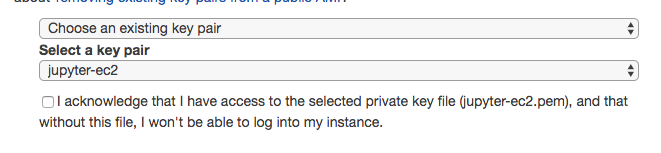
Setup ssh key (optional)
At local environment
|
|
Add this to end of file
1 2 3 4 5 |
Host jupyter
Hostname {ec2's public IP above}
IdentityFile {above downloaded key}
Port 22
User ec2-user |
Test access
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
$ ssh jupyter
Last login: Sat Feb 2 09:57:59 2019 from xxxx.xxxx.xxxx
__| __|_ )
_| ( / Amazon Linux 2 AMI
___|\___|___|
https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-2/
3 package(s) needed for security, out of 3 available
Run "sudo yum update" to apply all updates.
-bash: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directory
[ec2-user@ip-xxx-xxx-xxx ~]$ |
Setup jupyter
Install anaconda
1 2 3 4
$ mkdir Downloads $ cd Downloads/ $ wget https://repo.continuum.io/archive/Anaconda3-4.4.0-Linux-x86_64.sh $ bash Anaconda3-4.4.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
Generate ssl certificate
1 2 3
$ mkdir ~/certs $ cd ~/certs $ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:1024 -keyout mycert.pem -out mycert.pem
Generate password used when login
1ipython
1 2
from IPython.lib import passwd passwd()
You’ll see a sha1 hashed string in output. Save it for use at config step.
Config jupyter
Generate config file
1
|
$ jupyter notebook --generate-config |
Open setting file and add following text to the end
1
|
vim .jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
c = get_config()
# Kernel config
c.IPKernelApp.pylab = 'inline' # if you want plotting support always in your notebook
# Notebook config
c.NotebookApp.certfile = u'/home/ec2-user/certs/mycert.pem' #location of your certificate file
c.NotebookApp.ip = '*'
c.NotebookApp.open_browser = False #so that the ipython notebook does not opens up a browser by default
c.NotebookApp.password = u'{hashstring_above}' #edit this with the SHA hash that you generated after typing in Step 9
# This is the port we opened in Step 3.
c.NotebookApp.port = 8888 |
Set security group
Add port 8888 to access jupyter server
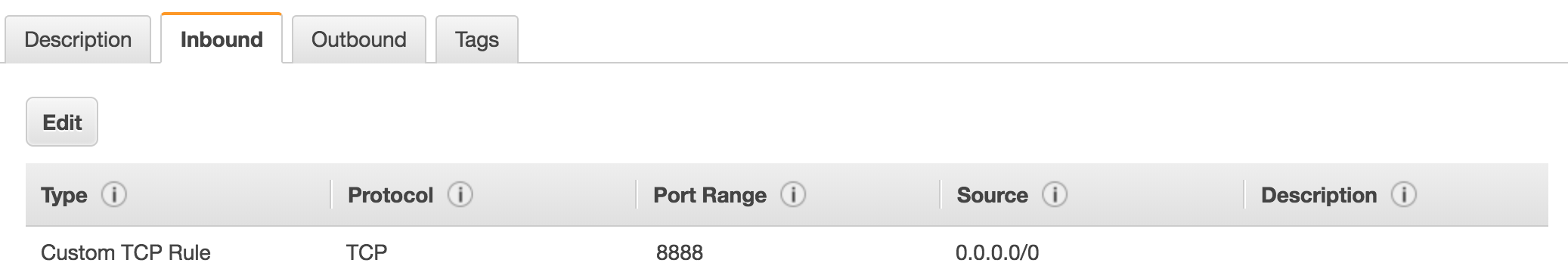
If you launched jupyter server at low port as 80, you need to add
sudowhen launch jupyter server. Source
Launch jupyter server
1 2 3 |
mkdir ~/Notebooks cd ~/Notebooks jupyter notebook |
Bonus
Auto start jupyter when instance is restarted
1 2 |
$ mkdir ~/scripts $ vi ~/scripts/jupyter-start.sh |
Add following text
|
|
Setup cronjob
1
|
@reboot /home/ec2-user/scripts/start_jupyter.sh > /dev/null |
Done
Enter your login password
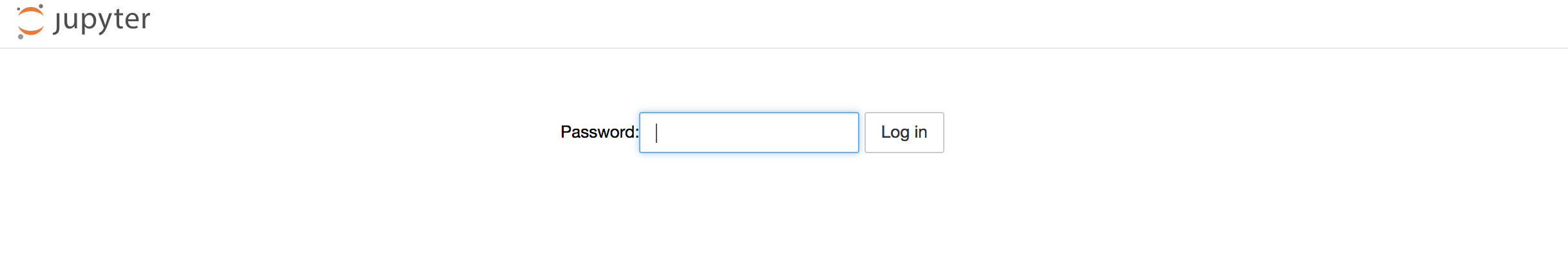
And
Author nhs000
LastMod 2019-02-02